
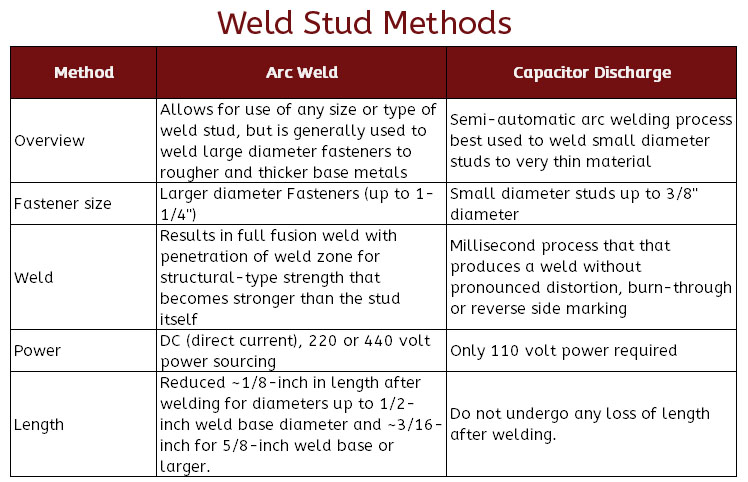
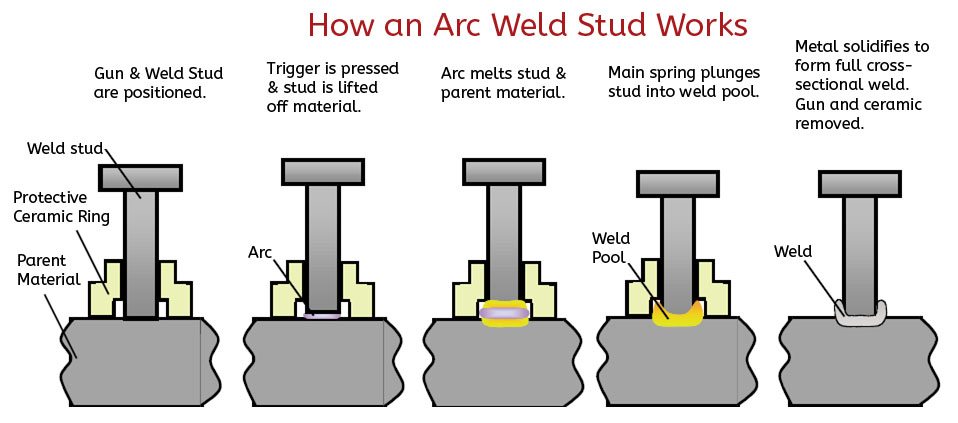
Weld studs are an ideal way to securely attached fasteners in extreme applications where reaching both sides of a structure is impossible or undesired. These weld studs can be attached by a variety of welding techniques, such as MIG or TIG welding or they can be attached by automated welding guns using Arc or Capacitor Discharge (CD) technologies. Weld Stud Sizes
o #4 - 4"
o M3 - M100 | Availability
Both fine and coarse threads available | Arc & Capacitive Discharge Weld Stud Benefits 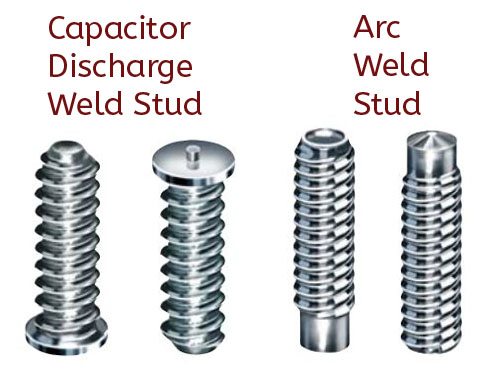 Security: Unlike the peripheral weld used on a common bolt, the weld used to secure a weld stud fastener is a full cross sectional weld, so the full face of the fastener is welded in place for a strong, secure hold. And since there are no drilled holes – which weakens the structural integrity of the application – the attachment is even stronger. Security: Unlike the peripheral weld used on a common bolt, the weld used to secure a weld stud fastener is a full cross sectional weld, so the full face of the fastener is welded in place for a strong, secure hold. And since there are no drilled holes – which weakens the structural integrity of the application – the attachment is even stronger.- Speed: Installing a weld stud is a fast and simple process with a most fasteners taking less than 1 second to weld in place. Plus there is no secondary work such as drilling, polishing or grinding.
- Simplicity: Weld studs require almost no special skills and minimal training and equipment is needed for installation. In addition, the equipment is also portable.
- Variety: Weld studs are available in a wide variety of fastener styles including (but not limited to) fully threaded, partially threaded, full base, reduced base, long, tapped base, and shoulder thread to name a few.
| Weld Stud Availability |




