Titanium Flat Head Screws
Unique for its strength, lightness of weight and corrosion resistance
- Lightweight and high strength
- Corrosion resistant to chlorides, sea water & chlorine
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Titanium grades, chemistry & specifications
- Titanium flat head screw features and benefits
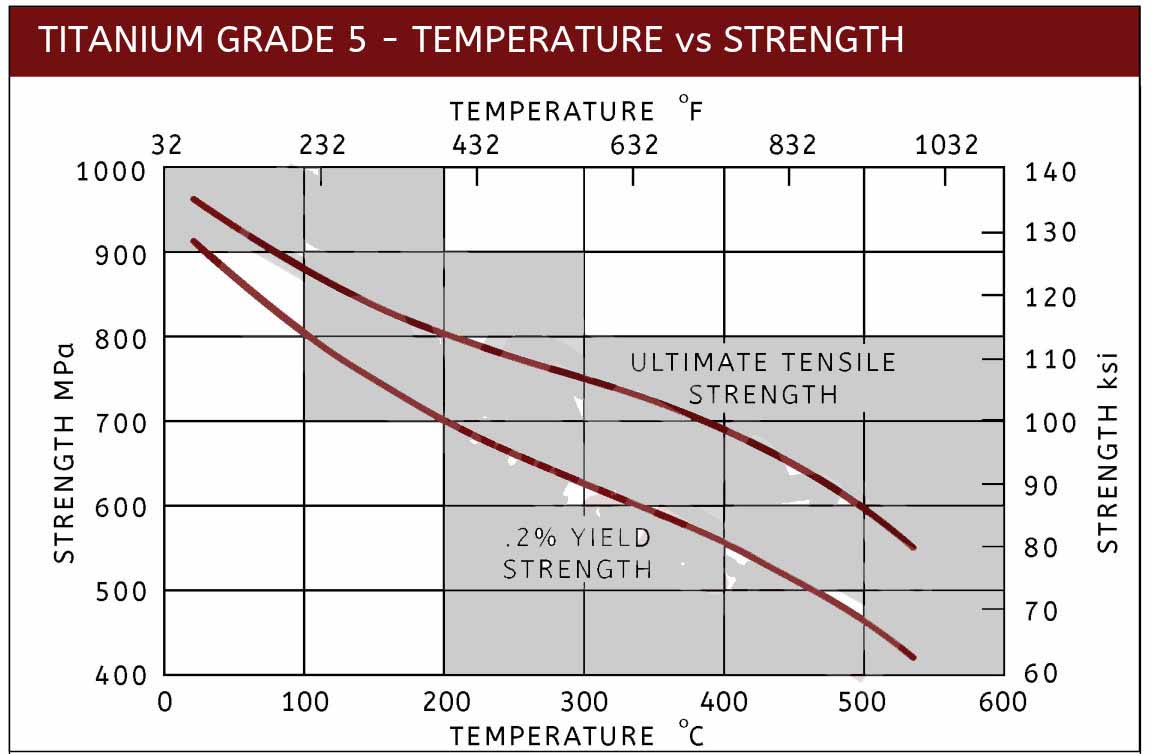
- Temperature vs strength data
- In-depth information on Grade 2 and Grade 5
Titanium flat head screws are best known for being strong, lightweight and corrosion resistant. One property that stands out when compared to other metal screws is that titanium screws have the highest strength-to-weight ratio with a density of 4.51 g /cm3. As an example, titanium grade 5 is 4 times stronger than 316 stainless steel at nearly half the weight. This makes titanium flat head screws ideal for applications that require both lightness of weight and excellent strength such as oil & gas (down-hole), military and sporting goods.
Titanium screws are also unique among metals in the chemical processing industry for handling chlorine (wet) and chlorine compounds in aqueous solutions. Titanium flat head screws are fully resistant to solutions of chlorides, hypochlorites, chlorates, perchlorates and chlorine dioxide. As a result titanium screws are often using within the chlorine related industries such as pulp and paper and chlor-alkali / bleach.
Titanium screws are also an excellent material to prevent seawater corrosion. Because titanium flat head screws can resists corrosion by seawater up to temperatures as high as 500°F (260°C) as well as survive at ocean depths over a mile below the surface, titanium screws are used throughout the oil & gas, desalination and marine industries.
The most common grades of Titanium flat head screws are Grade 2 and Grade 5. Gain more insight on these by accessing our Grade 2 and Grade 5 overviews or by contacting our engineering experts.
Resources: Titanium Torque Specs
Screw Types: 12 Point Screws, Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Head Cap Screws, Pan Head Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws, Torx Screws, Vented Screws
Titanium Flat Head Screw Features and Benefits
Titanium flat head screws are characterized by having a head with a top flat surface (which can feature either a slotted, phillips or allen driver) and bottom that is cone shaped or countersunk. With this design, the head of the screw can align flush or below the surrounding surface having obvious benefits.
Titanium Slotted vs. Phillips Driver
| Slotted Head Advantages | Phillips Head Advantages |
|
|
Countersink Angle
For most flat head screw designs the angle of countersink is usually 82° for UNC and UNF applications however other angles ranging from 60° -120° could be specified.
| Thread Type | Normal Flat Head Countersink Angle |
UNC / UNF | 82° |
| Aerospace | 100° |
| ISO Metric / Imperial | 90° |
Titanium Grades, Chemistry & Specifications
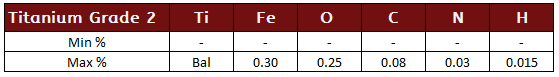
Titanium Grade 2 (Commercially Pure)
Unalloyed titanium; Commercially pure titanium is the most common grade of titanium utilized throughout industry due to its ease of availability and good properties.
Titanium Grade 2 Specifications: UNS R50400, ASTM B 348, AMS 4921, ASTM F 67, ISO 5832-2, Werkstoff 3.7035
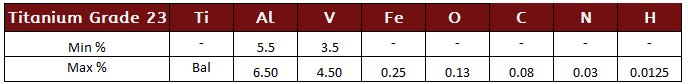
Titanium Grade 5 (Ti 6Al-4V)
Known as the “workhorse” of the titanium alloys, Ti 6Al-4V, or Grade 5 titanium, is 2x stronger than titanium grade 2. This alloy offers high strength and light weight, useful formability and high corrosion resistance. Ti 6AI-4V finds many uses in the aerospace, medical, marine and chemical processing industries.
Titanium Grade 5 Specifications: ASTM - B265, B348, B381, B861, F467 and F468, AMS - 4911, 4928, 4935, 4965 and 4967, MIL-T - 9046 and - 9047, Werkstoff 3.7165
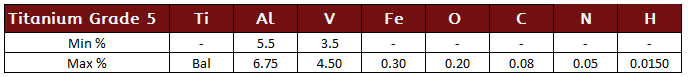
Titanium Grade 7
Grade 7 is the most corrosion resistant of all titanium alloys and is typically used in chemical processes and production equipment components. Similar to Grade 2, but with the addition of 0.12 to 0.25% palladium, Grade 23 has enhanced corrosion resistance to reducing acids and localized attack in hot halides.
Titanium Grade 7 Specifications: ASTM - B265, B337, B338, B348, B363, B381, B861 and B862, Werkstoff 3.7235
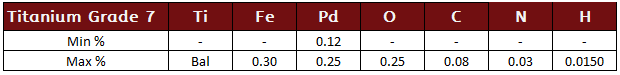
Titanium Grade 23 (TI 6AL-4V ELI)
Titanium grade 23 or TI 6AL-4V ELI is an Extra Low Intersticial grade. This grade is similar to Grade 5, but because of the low intersticials, its mechanical properties are enhanced. This ELI grade is often found in more demanding medical device applications as well as industrial applications.
Titanium Grade 23 Specifications:
ASTM - B265, B348, B363, B381, B861, B862 andF136, AMS - 4907, 4930 and 4956
Other titanium grades are also available upon request.
Mechanical Properties
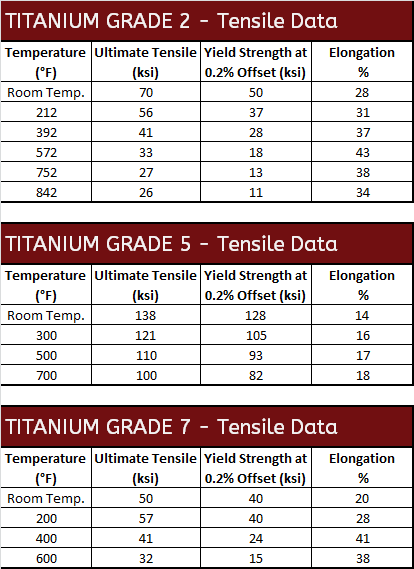
Titanium's Resistance to Chlorine
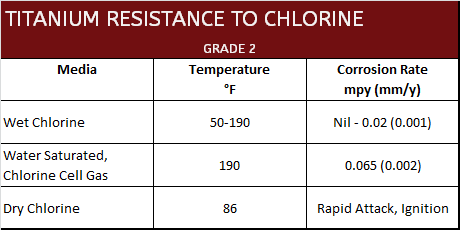
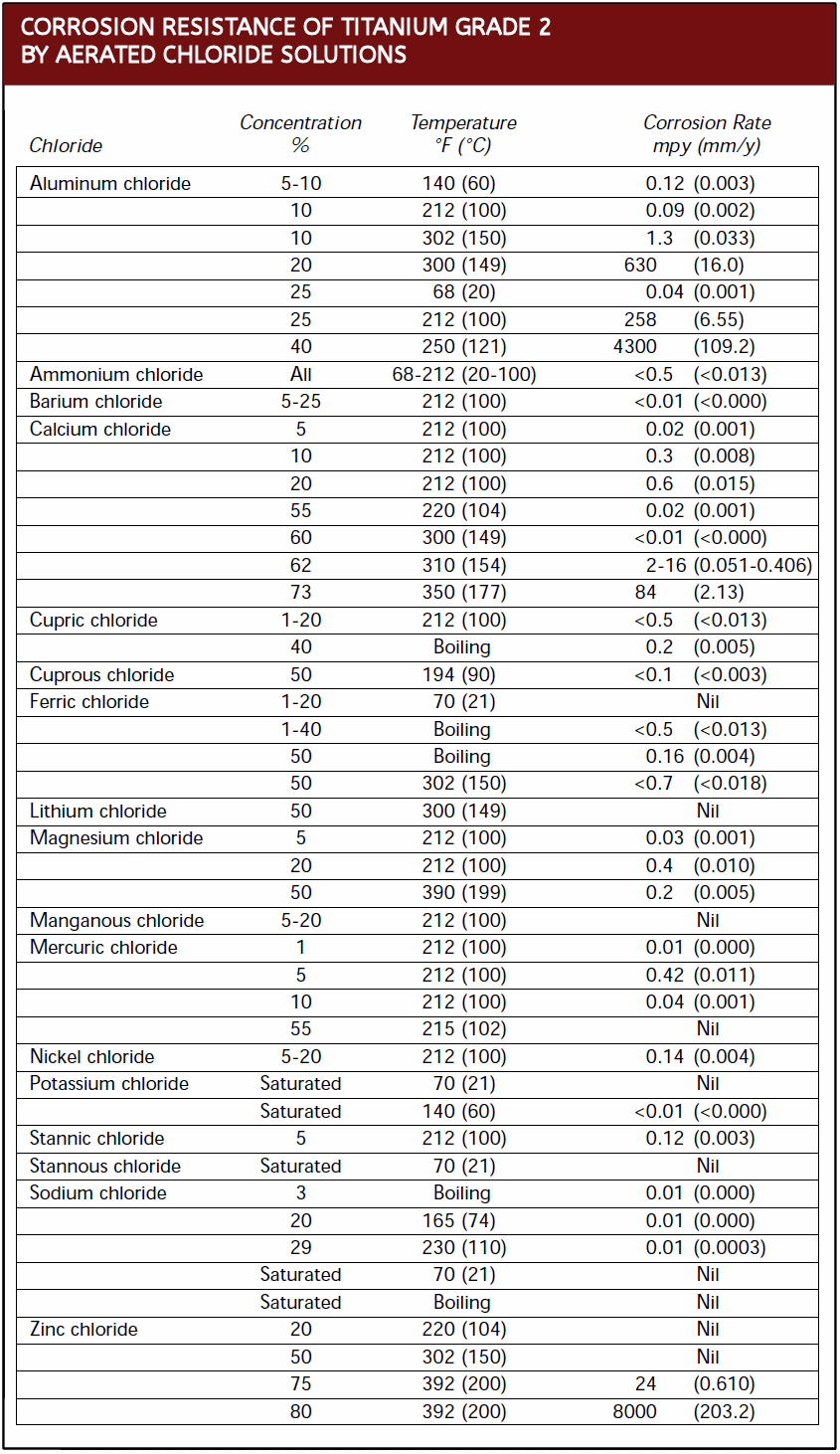
Corrosion Data
Titanium Grade 5 Temperature vs. Strength