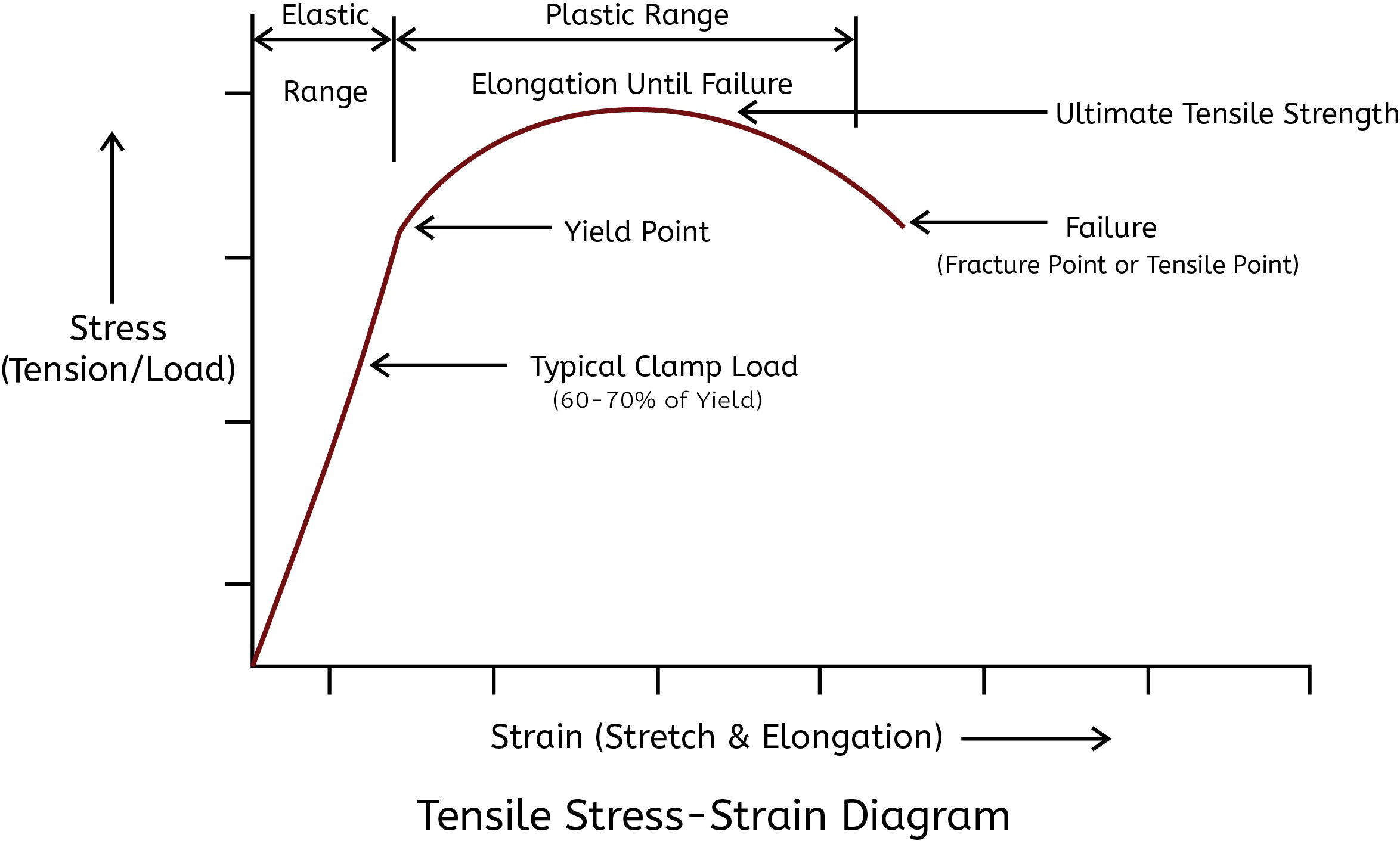
Torque is applied to the fastener in an effort to elastically deform the bolt shank. In the case of bolts and nuts, this elastic deformation between the bolt head and the nut is critical in order to create tension or clamping force to hold the joint together. The amount of torque applied is a function of the frictional forces and bolt diameter and is typically calculated utilizing a clamp load equaling 60-70% of the yield. Below are guides that show these calculations for a variety of materials, bolts sizes and thread counts over a range of frictional conditions.
NOTE: The actual clamp load is dependent on a variety of factors including the material, condition of the fasteners, surface finish, lubrication etc. The percentages provided are illustrative of what one might expect to see should only be used as a general guide. *Yield strength used to calculate torque values are based on the typical yield.*
CAUTION: Care should be used when applying a formula for torque/tension relationships. Torque is only an indirect indication of tension. Under/over tightening of fasteners can result in costly equipment failure or personal injury. All data included in this chart is advisory only and its use by anyone is voluntary. The data provided should be used as a guide, but actual material strengths and fastener conditions may vary. In developing this information, Special Fasteners China. & Fastener, LLC has made a determined effort to present its contents accurately.
Fastenal. (2009). [Illustration of Tensile: Stress-Strain Relationship] Bolted Joint Design: Mechanical Properties of Steel Fasteners in Service.
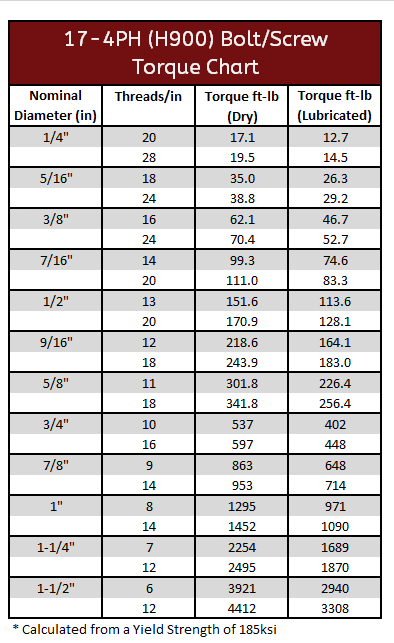
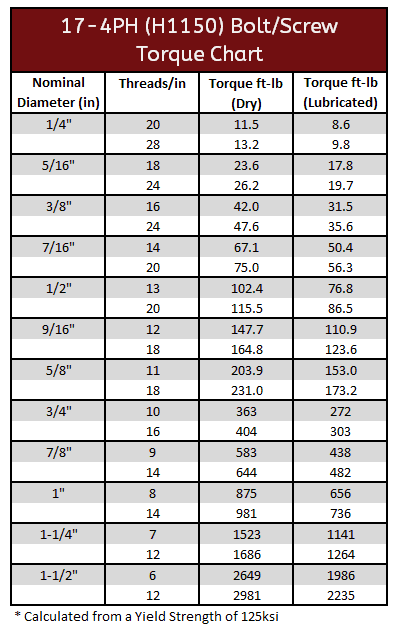
17-4 PH Torque Specification: H900 & H1150
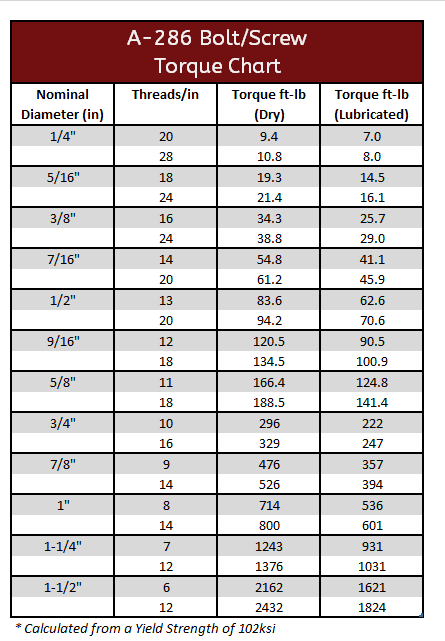
A-286 Torque Specification
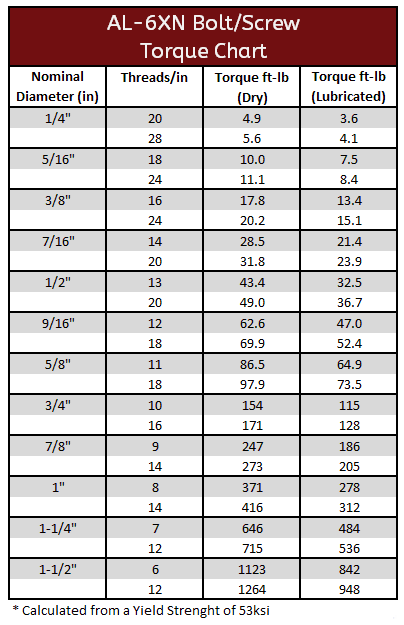
AL-6XN Torque Specification
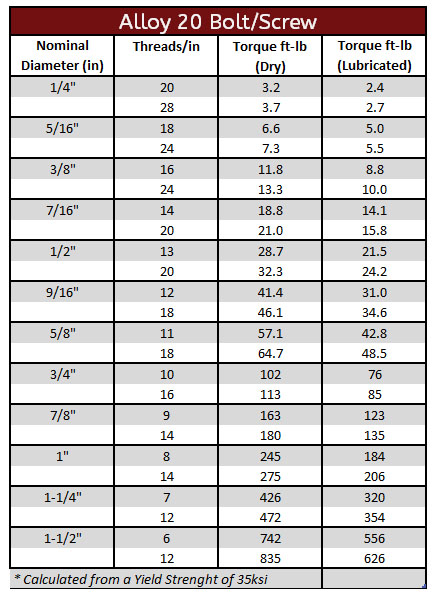
Alloy 20 Torque Specification
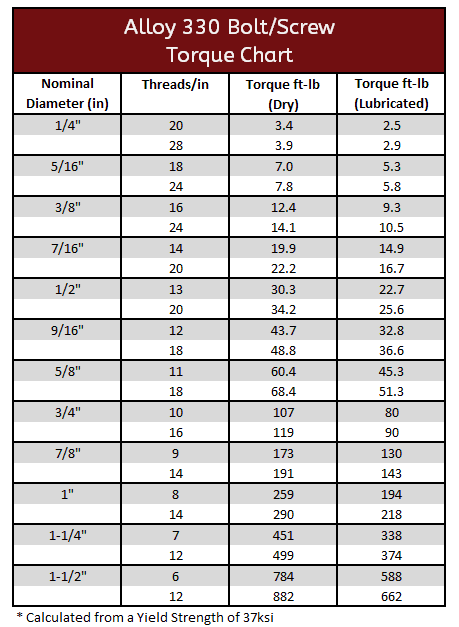
Alloy 330 Torque Specification
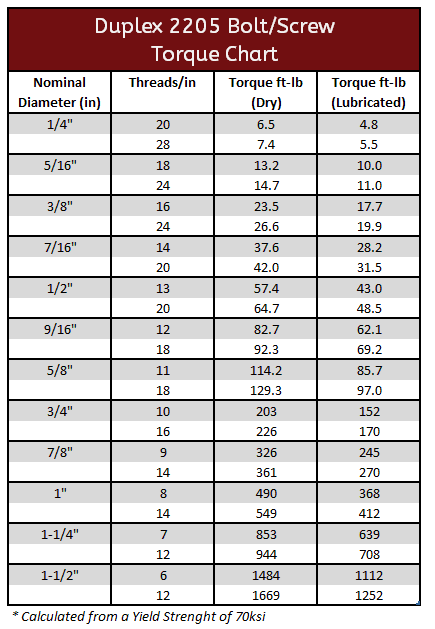
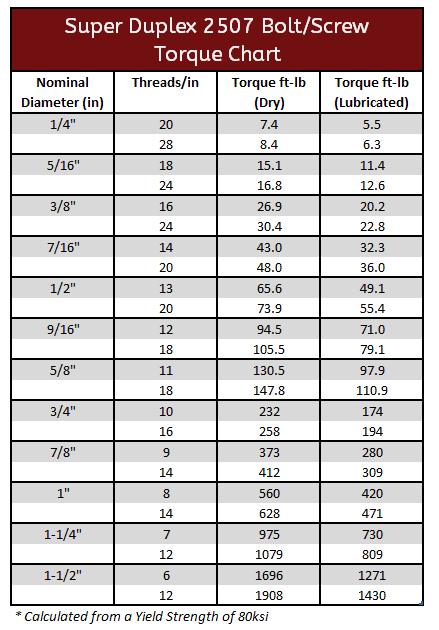
Duplex 2205 & 2507 Torque Specification
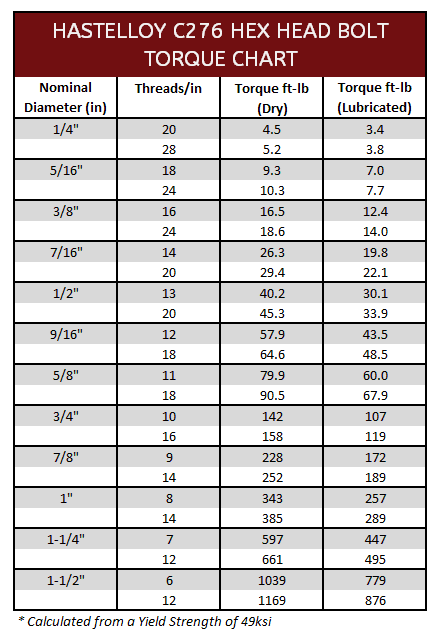
Hastelloy C276 Torque Specifications
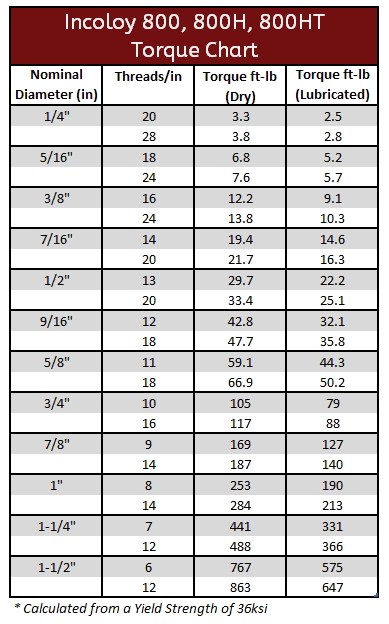
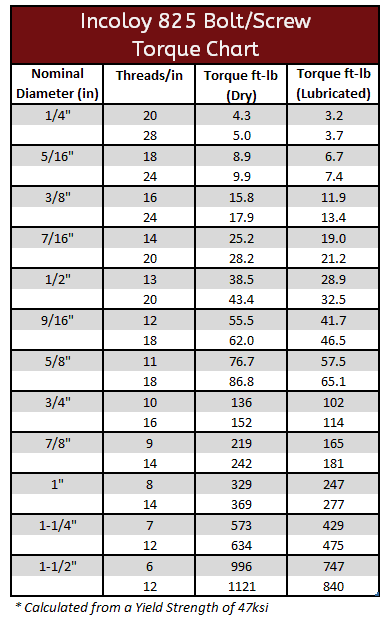
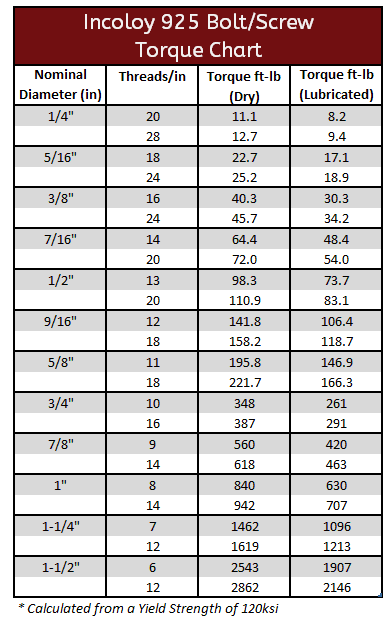
Incoloy Torque Specifications
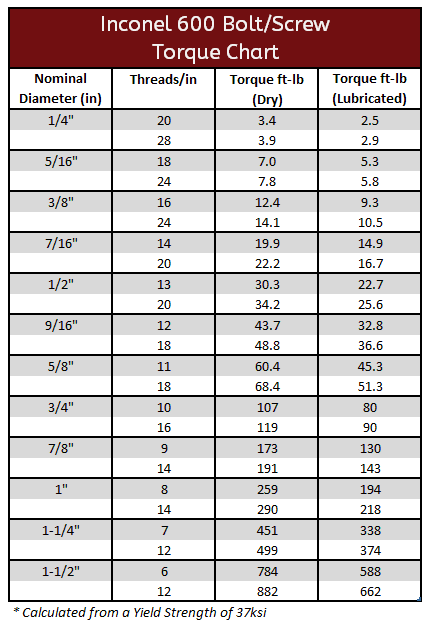
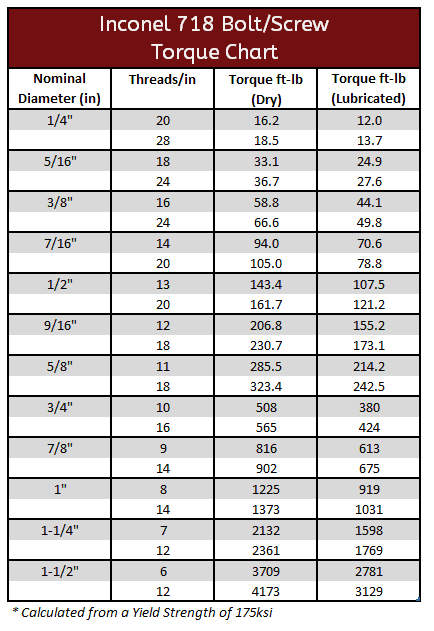
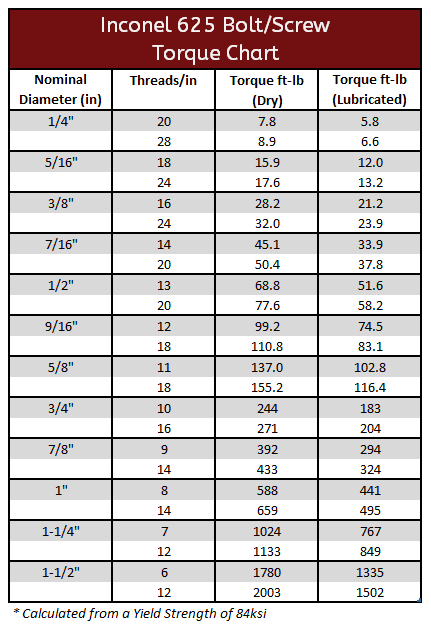
Inconel 600, 625 & 718 Torque Specifications
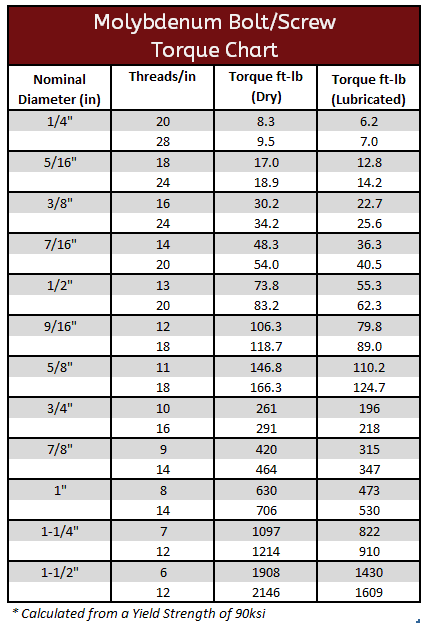
Molybdenum Torque Specifications
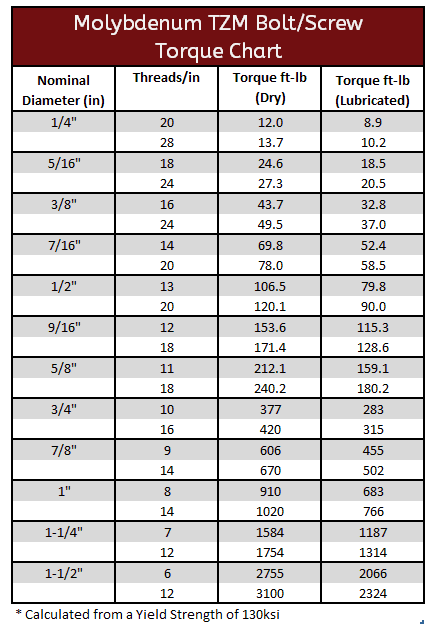
Molybdenum TZM Torque Specification
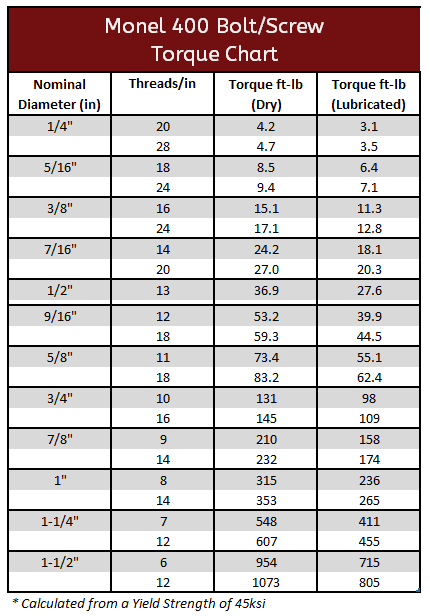
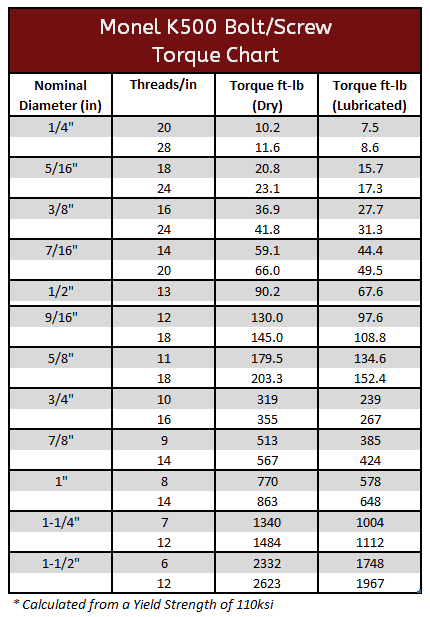
Monel 400 and K500 Torque Specifications
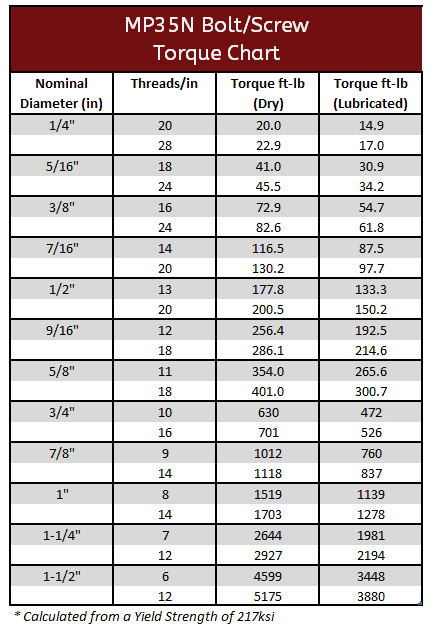
MP35N Torque Specifications
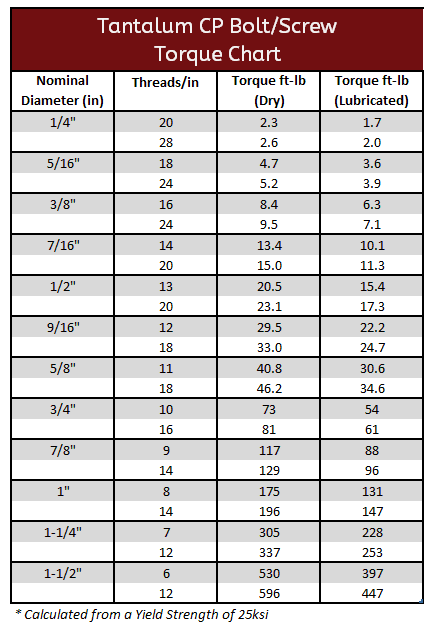
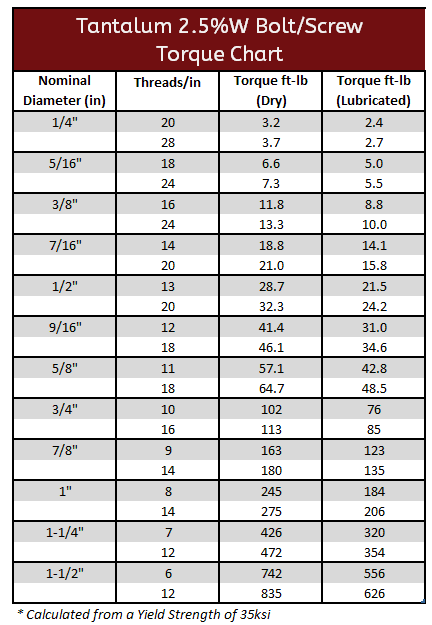
Tantalum CP & 2.5%W Torque Specifications
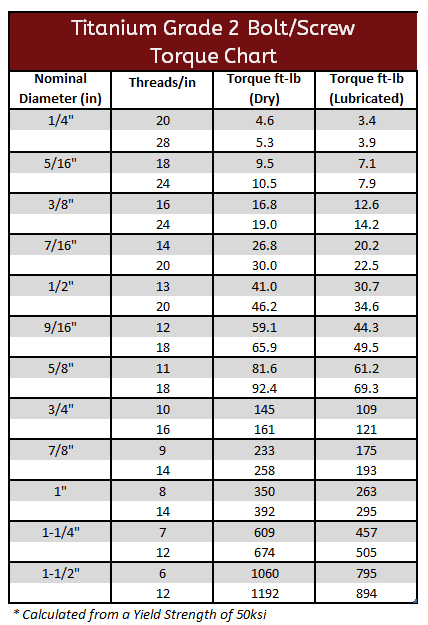
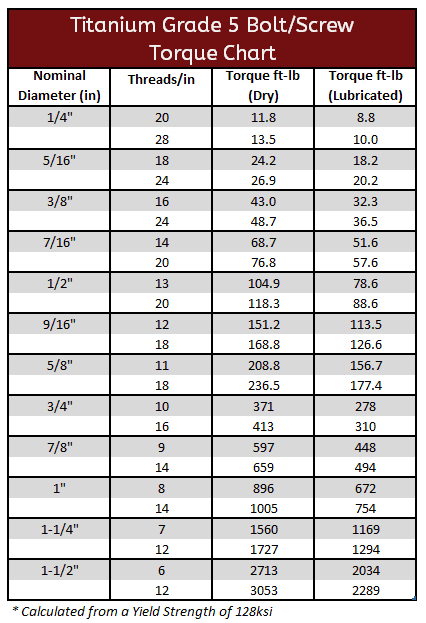
Titanium Gr2 & Gr5 Torque Specifications
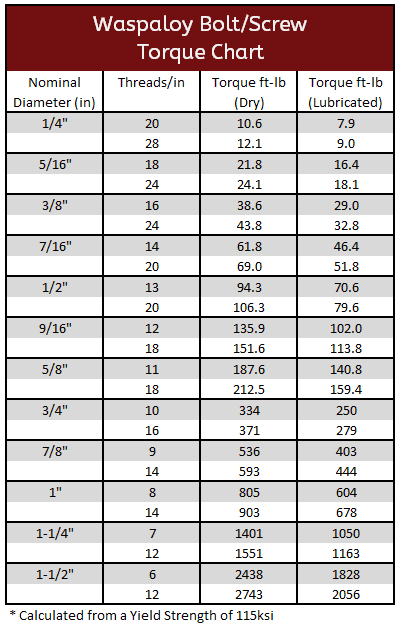
Waspaloy Torque Specification
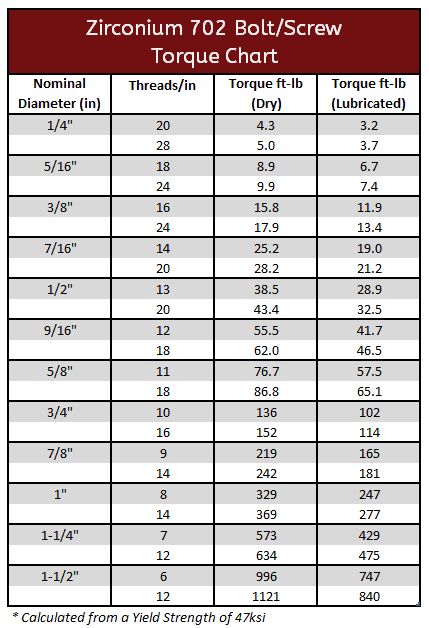
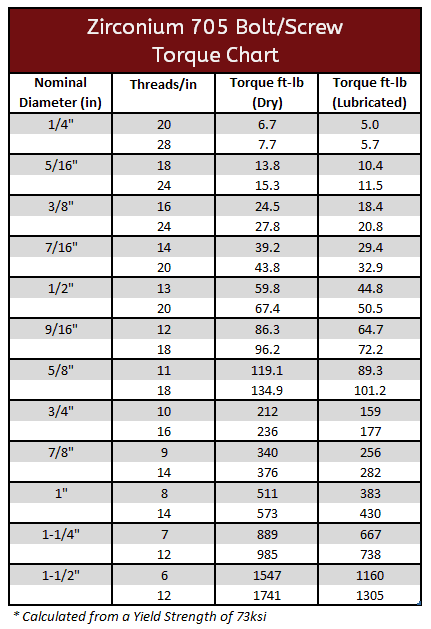
Zirconium 702 & 705 Torque Specifications

 Torque Calculator
Torque Calculator