When extreme high temperature stability & strength are required
- Maintains strength at elevated temperatures
- Low distortion at high temperature
- Molybdenum must be used in vacuum or inert gas at high temperatures
- Common molybdenum grades and specifications
- Molybdenum datasheet
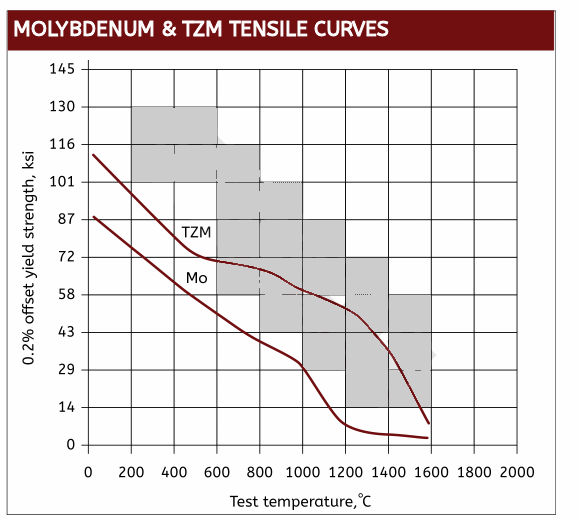
Molybdenum nuts possesses a very high melting point of 2620°C, a low coefficient of thermal expansion and a high level of thermal conductivity. Because molybdenum nuts have the ability to withstand extremely high temperatures without changing shape, expanding or softening significantly, they are ideal for high strength / high temperature applications that are shielded from oxygen. Exposing molybdenum fastener to oxygen above 600°C will cause them to readily oxidize.
As a result, molybdenum nuts find their way into high temperature vacuum furnaces, glass production, military and space applications where oxygen is not present.
Resources: Molybdenum Torque Spec
Nut Styles: Hex Nuts, Lock Nuts
Common Molybdenum Nut Grades and Specs
Molybdenum (Commercially Pure)
Because of its high melting point of 2620C and its good strength, pure molybdenum finds it niche in high temperature vacuum or inert environments without oxygen.
Molybdenum Specifications: ASTM B386, ASTM B387, Type 361

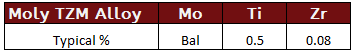
TZM - Titanium / Zirconium / Molybdenum Alloy
This alloyed version of molybdenum provides enhanced strenght at elevated temperatures and is excellent for support structures in vacuum furnaces or other high temperatuer and oxygen free environments.
TZM Specifications: UNS R03630, ASTM B384, ASTM B385, ASTM B386, ASTM B387
Mechanical Properties