A286 / Alloy 660 for excellent high temperature oxidation resistance
- Good material for high temperature oxidation resistance

- Maintains high strength at elevated temperatures
- Material specifications & heat treatments
- A286 specifications & heat treatments
- ASTM A453 Grade 660
- A286 Datasheet
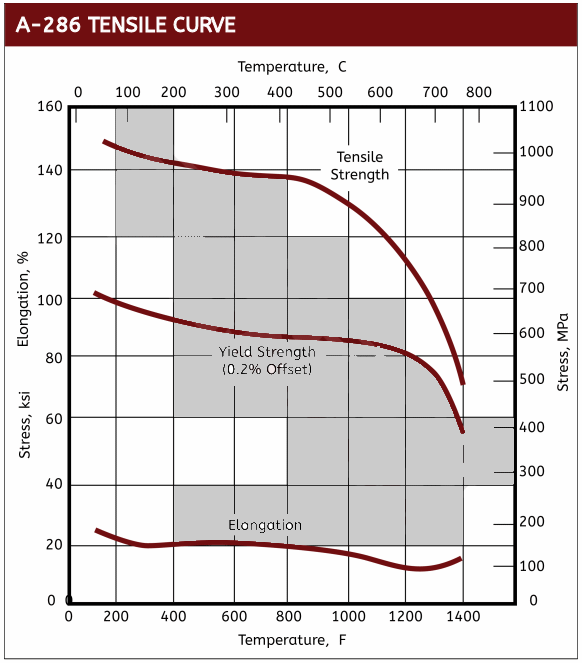
A286 screws, also known as Alloy 660 screws are stainless steel alloy which contains iron, nickel and chromium. A286 12 point screws are known for their high strength, creep resistance and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures once age hardened. As a result, A286 screws provide high levels of strength from room temperature up to about 1300°F (700°C).
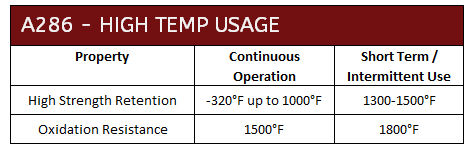
A286 12 point screws are also mildly corrosion resistant. While they should not be used for strong acid environments, they provide excellent oxidation resistance up to 1500°F (815°C) in conditions that would typically be found in high temperature exhaust streams.
Applications
Because of the properties of Alloy 660 / A286, these screws are often found in high temperature engine, manifold, exhaust and turbine applications as well as off-shore oil & gas applications. In addition, A286 / Alloy 660 is also non-magnetic and finds a niche in non-magnetic cryogenic equipment. For the most sensitive applications, we can also provide A286 bolts and fasteners per ASTM A453 Grade 660 specification. This provides specific paraments to ensure tensile strengths and rupture properties.
Resources: A286 Torque Specs
Screw Types: 12 Point Screws, Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Cap Screws, Pan Head Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws, Torx Screws, Vented Screws
A286 / Alloy 660 12-Point Screw Features & Benefits
The driver of a A286 12-point screw uses two overlapped hexagon shapes, creating 12-points and a flanged underside. These are also referred to as ferry cap screws or 12 point flange screws. The advantages of this head style include:
- Higher torque capability compared to a socket head cap screw
- Lack of recess to trap fluid or debris.
- As the heads are generally smaller than a hex, A286 / Alloy 660 12-point screws are often used situations where installation space is tight and saving weight is critical.
The overall disadvantage is the extra cost involved in forming the heads.
The Controversy of 6 vs. 12 point Bolts
There is much debate over which bolt is better. Some say that the more points a nut or bolt has – such as a 12-point bolt - the less chance you have to round it off. And that the additional contact points of a 12 point screw give you more surface to apply load. While the jury is out as to the accuracy of this, it’s the application that should dictate whether the benefits of a 12 point screw out weight the additional costs of making them.
ASTM A453 Grade 660
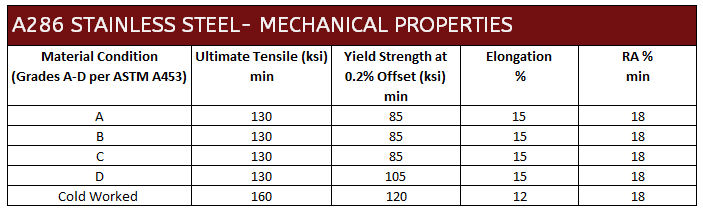
Material specification ASTM A453 Grade 660 applies to bolts, studs, studs and other fasteners. It ensures fasteners meet strength standards for use in high temperature bolting applications. ASTM A453 Grade 660 is classified into 4 property classes / heat treatments: A, B, C & D, each designated with different tensile and stress rupture properties. The most common of the ASTM 453 classes are class A or D. The grades A, B and C all have the same minimum tensile strength and minimum yield strength of 130ksi and 85ksi respectively. However grade D has a significantly better yield with a min tensile of 130ksi and a min yield of 105ksi.
Additional A286 / Alloy 660 Specifications, Cold Working & Heat Treatments
AMS A286 / Alloy 660 Heat Treatments
By AMS numbers, the most common for A286 / Alloy 660 is AMS 5737 (same as Grade A) and then AMS 5732 (same as Grade B).
A286 / Alloy 660 Cold Worked Fasteners
For additional strength, A286 could be aged and cold worked to achieve a min ultimate tensile strength of 160ksi upon request.
Additional Specifications
UNS S66286, ASTM A453, AMS 5525, AMS 5726, AMS 5732, AMS 5737, AMS 5804, EN 1.4980, GE B50T1181, GE B50T12, GE B50T81, Werkstoff 1.4980, ASTM F2281
A286 / Alloy 660 Chemistry
Mechanical Properties