A Ni-Cr alloy with very good high temperature stability
 Good high temperature strength
Good high temperature strength- Oxidization and carburization resistant at high temperatures
- Good corrosion resistance, which increases with the various grades
- Lap joint flange features and benefits
- Download our Incoloy datasheets for more indepth technical information.
Not to be confused with Inconel, Incoloy flanges are made of a nickel alloy which contains iron and a lower content of nickel. Incoloy is essentially a more economical option to Inconel, yet with more restricted corrosion resistance and temperature limits. Typically, Incoloy is an ideal material for long-term exposure in high temperature environments due to its oxidation, carburization and creep resistance. Incoloy is widely used for its resistance to seawater, brine, sour gas and high chloride environments at elevated temperatures, which make it a popular choice in the oil and gas and power industries.
The most commonly used grades of Incoloy flanges are Incoloy 800, 800H, 800HT;Incoloy 825; and Incoloy 925. For more indepth information on these specific grades, visit our specific web pages or contact one of our engineering experts:
Datasheets: Incoloy 800, 800H 800HT; Incoloy 825; and Incoloy 925
Resources: Incoloy Torque Specs, Flange Dimensions, Flange Bolting Chart
Incoloy Fastener Types: Bolts, Nuts, Screws, Threaded Rods, Washers
Flange Types Available: Blind Flanges, Slip On Flanges, Socket Weld Flanges, Threaded Flanges, Weld Neck Flanges
Common Incoloy Chemistry, Grades & Specifications
Incoloy 800, 800H, H00HT
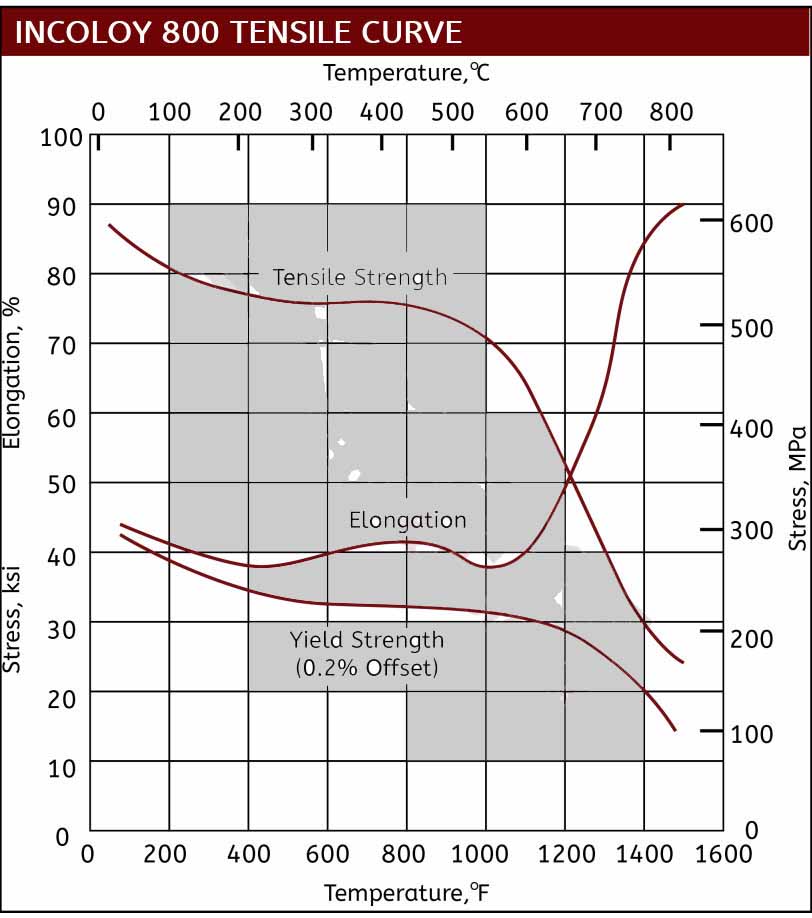
Incoloy 800 series flanges are best utilized for applications that require stable structure and good strength during prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Incoloy 800, 800H & 800HT Specifications: UNS N08800/ N08810 / N08811 (800, 800H, 800HT), ASTM B408, ASME SB408, ASTM B564/ASME SB564, EN 10204-3.1, Werkstoff 1.4876 (800), Werkstoff 1.4876 H and 1.4958 (800H), Werkstoff 1.4876 HT and 1.4959 (800HT)
Incoloy 825
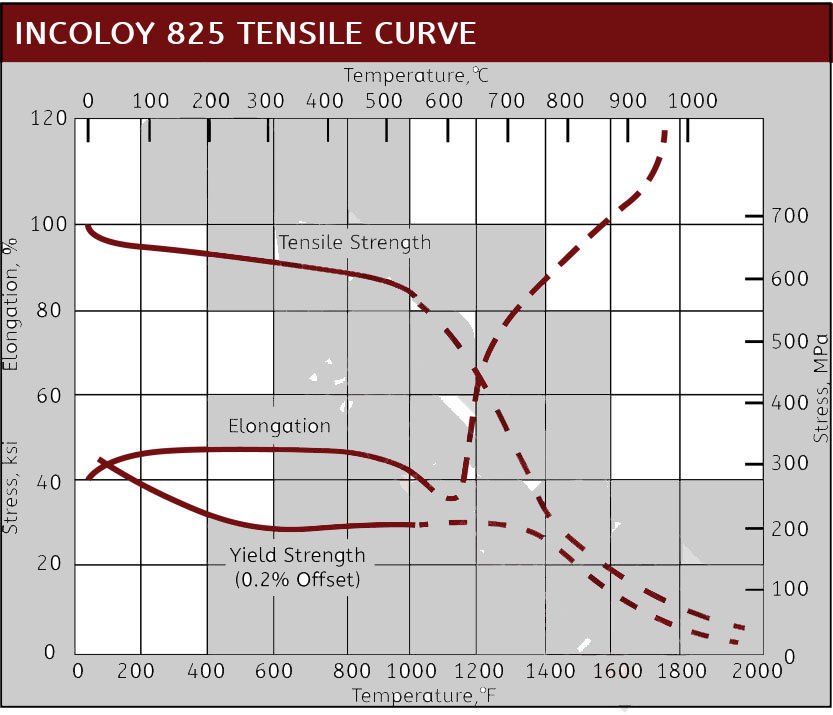
Related to the Incoloy 800 series alloys, Incoloy 825 differentiates itself with the additional elements of molybdenum and copper, which provides it improved corrosion resistance.
Incoloy 825 Specifications: UNS N08825, , BS 3076NA16, ASTM B 425, ASTM B 564, ASME SB 425, ASME SB 564, ASME Code Case N-572, DIN 17752, DIN 17753, DIN 17754, VdT"UV 432, ISO 9723, ISO 9724, ISO 9725, Werkstoff Nr 2.4858

Incoloy 925
Incoloy 925 is a precipitation hardened alloy. It offers comparable corrosion resistance to it’s sister alloy Incoloy 825, but with the increased strength resulting from the age hardening process.
Incoloy 925 Specifications: UNS N09925, ASTM B637, NACE MR0175 
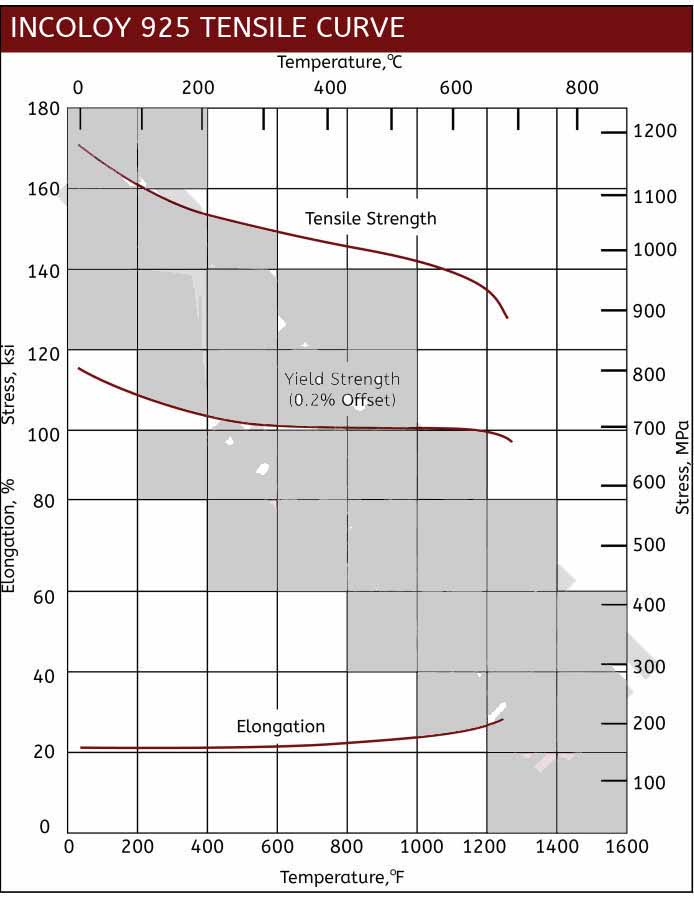
Mechanical Properties of Incoloy
Incoloy Lap Joint Flange Features & Benefits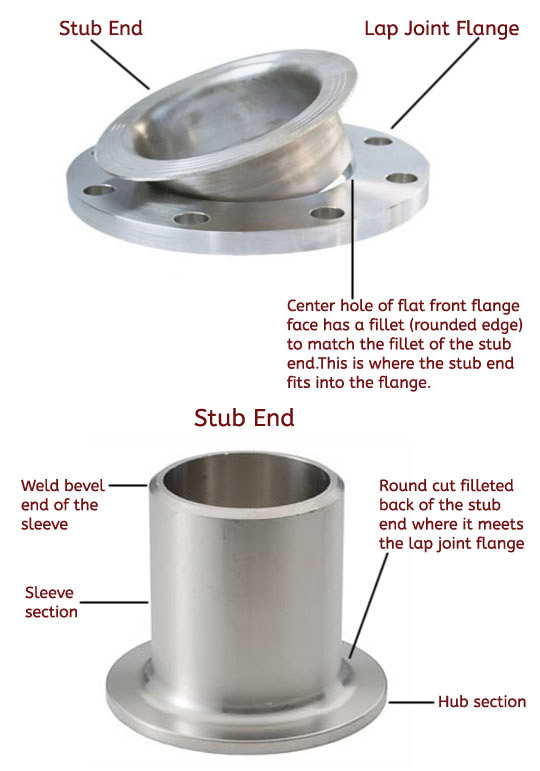
Lap joint flanges are unique in that they are made of two pieces, the flange itself and the stub end.
Flange
- The backside, has a slight shoulder that is square cut at the center or pipe hole
- The front side has a flat face with a filleted (rounded) center hole to match the filleted back face of the stub end. Here the stub end will wrap tightly around the center hole of the flange.
Stub End
- Shaped like a short piece of pipe with a weld bevel on one. This portion of the stub end is also called the sleeve.
- Narrow shoulder on the flange facing end called is the hub. The back face of the hub has a rounded transition (or inside fillet) that joins the hub to the sleeve
Benefits
- Economy
Because a lap joint flange has a two piece configuration, it offers a way to cut cost when piping systems requires - For high cost alloys the only "wetted" part is the stub end. In this situation, it is only required for the stub-end to be made of the higher cost corrosion-resistant material, where the flange itself can be the produced from lower cost steel.
- Ease of Work
By using lap joint flanges, work can be simplified in situations that require frequent and rapid disassemble and assembly during the operation of a plant. The ability to spin that backing flange compensates for misalignment of the bolt holes during assembly.
